- Introduction: Smart Grid Integration with AI
- What is a Smart Grid?
- Why Smart Grids Need AI
- Core Benefits of AI Integration in Smart Grids
- AI Applications in Smart Grids
- Key AI Technologies Used
- Challenges in Integration
- Global Case Studies & Success Stories
- Future Trends in AI for Power Systems
- How to Get Started with AI-Enabled Smart Grids
- Final Thoughts + Action Plan
Introduction: Smart Grid Integration with AI
You’ve probably heard the term “smart grid” thrown around in energy discussions. It’s true — smart grids are a major upgrade from traditional grids. But here’s the thing: they still fall short without intelligence. That’s where Artificial Intelligence (AI) comes in.
In this article, we’ll break down exactly how AI transforms smart grids from reactive systems into predictive, self-healing networks, dramatically improving sustainability, reliability, and cost-efficiency.
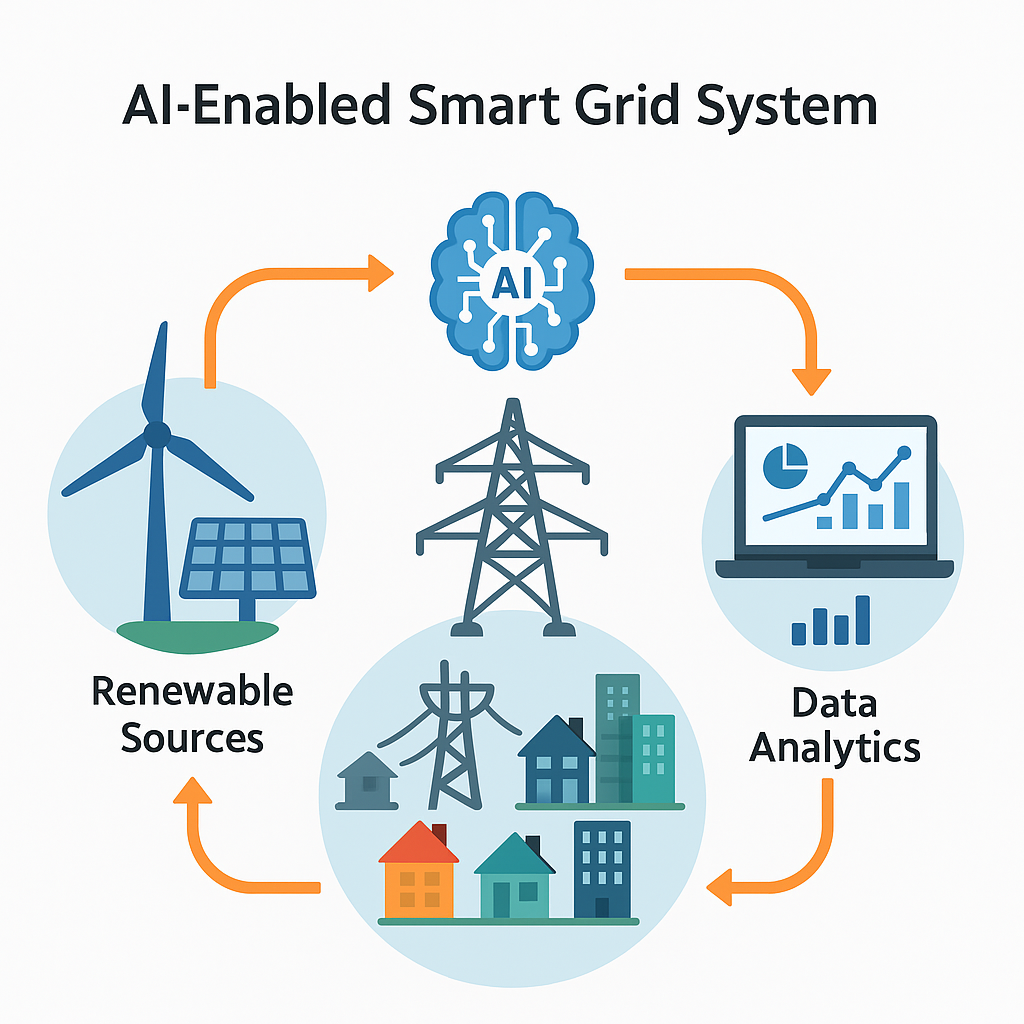
What is a Smart Grid?
A smart grid is a modern electrical grid that uses digital communication technology to detect and react to local changes in usage.
Traditional Grid vs. Smart Grid:
| Feature | Traditional Grid | Smart Grid |
|---|---|---|
| Data Flow | One-way | Two-way |
| Monitoring | Manual | Real-time |
| Outage Response | Slow | Automated |
| Load Management | Static | Dynamic |
Why Smart Grids Need AI
While smart grids can collect and transmit data, they don’t have the brainpower to analyze or act on it at scale. That’s the missing link — AI fills this gap.
With AI, a smart grid can:
- Predict energy demand.
- Automate load balancing.
- Optimize renewable energy usage.
- Prevent blackouts before they occur.
Core Benefits of AI Integration in Smart Grids
Enhanced Grid Reliability
AI can forecast equipment failure and reduce unplanned downtime by up to 30%.
Real-Time Load Balancing
AI enables dynamic energy routing. That means power flows where it’s needed most — instantly.
Cost Reduction
Utility companies can cut operational costs through AI-driven predictive maintenance and energy theft detection.
Greater Renewable Integration
Solar and wind are intermittent. AI smooths their output using forecasting and battery optimization.
AI Applications in Smart Grids
Let’s get into the meat.
Demand Forecasting
Using historical data, weather forecasts, and real-time consumption, AI models predict future demand, helping utilities plan accordingly.
Fault Detection & Prediction
AI algorithms spot patterns in sensor data and detect anomalies before failure happens.
Think of it like your car telling you the engine is going to fail days before it actually does.
Energy Theft Detection
AI uses pattern recognition to catch non-technical losses, such as meter tampering.
Distributed Energy Resource (DER) Management
Managing rooftop solar panels and EV chargers? AI can orchestrate these DERs into a cohesive network.
Key AI Technologies Used
| AI Tech | Use Case in Smart Grid |
|---|---|
| Machine Learning | Forecasting load, pricing, equipment health |
| Deep Learning | Image recognition from drones, pattern detection |
| Reinforcement Learning | Real-time control & automation |
| Natural Language Processing (NLP) | Chatbots for customer service, document parsing |
Challenges in Integration
Let’s not sugarcoat it. AI in smart grids isn’t plug-and-play.
Data Privacy Concerns
Consumer energy usage data is sensitive. AI systems need robust cybersecurity frameworks.
Data Silos
Many utilities still have fragmented systems that don’t talk to each other. AI needs consolidated datasets to work effectively.
Skill Gap
There’s a lack of engineers who understand both power systems and data science.
Global Case Studies & Success Stories
Canada: Hydro-Québec
Hydro-Québec uses AI to predict and manage ice storm risks, reducing outages by over 40%.
UK: National Grid ESO
Uses AI for grid balancing in real time, particularly during high renewable penetration.
US: Pacific Gas and Electric (PG&E)
Leverages AI for wildfire risk assessment based on weather, vegetation, and grid load.
Future Trends in AI for Power Systems
- Edge AI: Processing directly at sensors for faster response times.
- AI + Blockchain: Secure, decentralized energy transactions.
- Autonomous Grids: Self-healing grids that require minimal human intervention.
- AI-powered EV Charging: Optimizing when and how EVs charge based on grid status.
How to Get Started with AI-Enabled Smart Grids
Step 1: Digitize the Grid
Before AI, you need data. Install smart meters, IoT sensors, and digital substations.
Step 2: Consolidate Your Data
Break down silos. Use cloud platforms to centralize your data.
Step 3: Start with Low-Risk AI Projects
Begin with forecasting or maintenance prediction before moving to automation.
Step 4: Upskill Your Team
Train your engineers in AI, machine learning, and data analytics.
Final Thoughts + Action Plan
Smart grids are the future — but without AI, they’re blind.
If you’re a utility, energy consultant, or engineer, the opportunity to lead in AI-powered grid innovation is massive. Start small, iterate fast, and focus on use cases that bring ROI.